Differentiating Pudendal Nerve Entrapment (PNE) from Other Pelvic Conditions
Diagnosing pudendal nerve entrapment can be challenging because its symptoms often mimic those of other pelvic disorders, such as:
- Piriformis syndrome
- Interstitial cystitis
- Vulvodynia
- Prostatitis
Prostatitis, a condition often heard of but seldom fully understood, predominantly affects the male population, specifically the prostate gland. This condition is characterized by inflammation or infection of the prostate gland and can significantly impact the quality of life. In this article, we explore the nuances of prostatitis, delve into the various treatment modalities available, and finally, draw distinctions between prostatitis and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a condition often confused with prostatitis due to the similarity in the affected region and some overlapping symptoms.
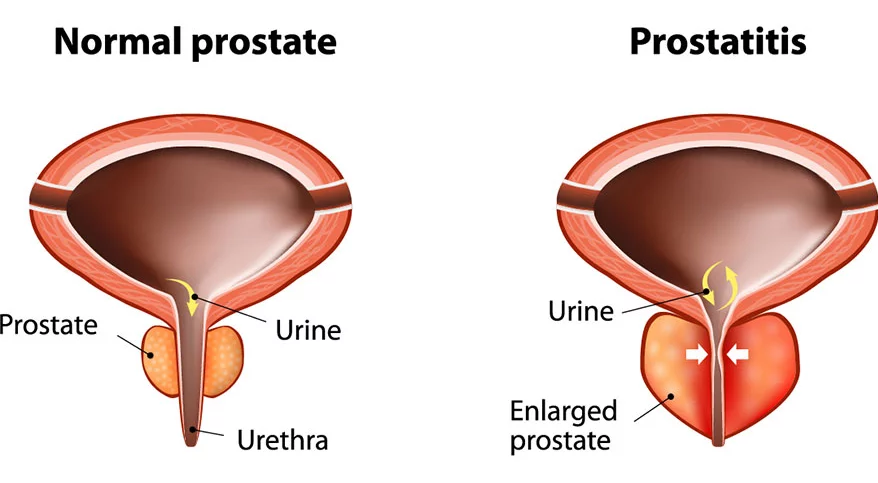
Prostatitis
Prostatitis refers to a group of conditions characterized by inflammation or infection of the prostate gland. It can present in various forms, including acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome, and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis. The symptoms can vary widely, ranging from pain and discomfort in the pelvic area, lower back, and genital area to urinary symptoms like increased frequency, urgency, and painful urination. The exact etiology remains elusive for certain forms, especially chronic prostatitis, but bacterial infections often cause acute forms of the condition.
Prostatitis Treatment
Treating prostatitis involves addressing the underlying cause and managing the symptoms.
- Antibiotics:
– They are the first line of treatment for bacterial prostatitis, and the duration of treatment may vary depending on the severity and type of infection.
- Alpha Blockers:
– Medications like tamsulosin can help relax the bladder neck and the muscles where the prostate joins the bladder, alleviating urinary symptoms.
- Anti-Inflammatory Agents:
– Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be used to manage pain and inflammation associated with prostatitis.
- Prostate Massage:
– Some healthcare providers might suggest prostate massage to help relieve symptoms, especially in cases of chronic prostatitis.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
– Regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding alcohol, caffeine, and spicy foods can play a crucial role in managing symptoms.
Prostatitis vs BPH
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), also known as prostate gland enlargement, is another common condition affecting older men. Though it shares some symptoms with prostatitis, like urinary frequency and difficulty in urination, the two are distinct conditions.
- Etiology:
– While prostatitis is mainly caused by bacterial infection or inflammation, BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland due to aging and changes in cell growth.
- Age of Onset:
– Prostatitis can affect men of all ages but is more common in young and middle-aged men. In contrast, BPH predominantly affects older men, usually those above 50.
- Treatment:
– The treatment for BPH includes medications to relax the prostate muscle fibers, surgery to remove enlarged prostate tissue, and lifestyle modifications.
– Prostatitis treatments, conversely, are more oriented toward resolving infections and managing inflammation and pain.
- Symptoms:
– Though both conditions present with urinary symptoms, prostatitis may also be associated with pain in the pelvic area, fever, and chills, especially in acute cases.
Prostatitis, a condition that can significantly impact one’s quality of life, demands attention and understanding due to its potential complexity and varied manifestations. Effective treatment hinges on accurate diagnosis and comprehensive management strategies, including medication, lifestyle modifications, and in some cases, procedural interventions. Furthermore, distinguishing between prostatitis and BPH is crucial for appropriate management and treatment, given the overlapping symptoms but different underlying causes and treatment approaches. A thorough understanding of these conditions can empower individuals to seek timely and appropriate care, thereby improving their quality of life.
