Prostatitis, a complex condition affecting men, involves inflammation or infection of the prostate gland. This article delves into prostatitis treatments, shedding light on the distinctive nature of this ailment and addressing its connection to Pudendal Neuralgia. Understanding the interplay between prostatitis and pudendal neuralgia is crucial, considering the impact on discomfort, pain, urinary symptoms, and sexual dysfunction.
Understanding Prostatitis

Prostatitis, a multifaceted condition predominantly affecting the male population, is defined as the inflammation or infection of the prostate gland. This walnut-sized gland, situated just below the bladder, plays a crucial role in male reproductive health. Prostatitis is not a single disorder but a spectrum of conditions, each presenting distinct characteristics and complexities.
Types of Prostatitis
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, scientists have determined four different types of prostatitis:
-
Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
Acute bacterial prostatitis, a severe form of the condition, results from a sudden bacterial infection in the prostate. Symptoms include a high fever with chills, intense pelvic pain, painful urination, and increased urinary urgency. Systemic effects like fatigue and muscle aches may accompany them. Prompt medical attention is crucial to preventing complications such as abscess formation and systemic infection.
-
Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
Similar to its acute counterpart, chronic bacterial prostatitis results from persistent bacterial infections within the prostate. However, this form extends over a more prolonged duration, featuring recurrent infection episodes. The symptoms may be less severe than in acute cases, but the persistence of infection can lead to a continuous cycle of flare-ups, requiring long-term management with antibiotics. Individuals may experience intermittent exacerbations of symptoms, including pelvic pain, urinary issues, and discomfort.
-
Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CP/CPPS)
Chronic prostatitis, particularly chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS), presents a prevalent and complex challenge characterized by persistent pelvic discomfort lasting at least three months. Unlike bacterial forms, CP/CPPS lacks clear evidence of ongoing infection, exhibiting variable symptoms including pelvic pain, urinary issues, and sexual dysfunction.
Management requires a multifaceted approach, addressing both physical and psychological aspects through medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications for comprehensive well-being. Navigating the intricacies of CP/CPPS demands a personalized and multidisciplinary strategy to effectively address its nuanced challenges.
-
Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis
In asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis, inflammation is present within the prostate gland, but individuals do not experience noticeable symptoms. This form is typically diagnosed incidentally during medical investigations for other conditions.
It underscores the silent nature of certain prostatic inflammations, highlighting the importance of a thorough examination, even in the absence of overt symptoms. Understanding the diverse presentations of prostatitis is crucial for tailoring effective treatment strategies based on the specific characteristics of each form.
Symptoms and Manifestations
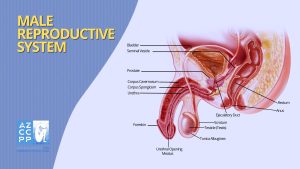
Prostatitis, a multifaceted condition affecting men, exhibits a diverse range of symptoms that can significantly impact daily life.
-
Pelvic Pain or Discomfort
Pelvic pain associated with prostatitis is often characterized by persistent, aching discomfort in the pelvic region. This can extend to the perineum, lower abdomen, and rectal area, creating a sensation of pressure or fullness. For instance, individuals may describe it as a dull, throbbing ache that varies in intensity.
-
Lower Back Pain
Prostatitis-related lower back pain manifests as a deep, persistent ache in the lumbar region. This discomfort may radiate from the pelvic area, contributing to an overall sense of heaviness or soreness in the lower back.
-
Genital Pain
Genital pain associated with prostatitis involves discomfort in the testicles, penis, or scrotum. This pain can be described as a dull ache, tenderness, or a throbbing sensation, impacting both physical and psychological well-being.
-
Painful Urination
Painful urination, a hallmark symptom, results from the inflammation of the prostate. This discomfort can range from a burning sensation to sharp pain during urination, affecting the overall urinary experience.
-
Increased Urinary Frequency
Prostatitis often leads to an increased urge to urinate, compelling individuals to visit the restroom more frequently than usual. This heightened urinary frequency disrupts daily activities and can be particularly bothersome.
-
Urgency to Urinate
The urgency to urinate is another common symptom, where individuals experience a compelling and sudden need to empty their bladder. This urgency can be disruptive and may cause anxiety in social situations.
-
Systemic Symptoms in Acute Cases
Acute prostatitis may present with systemic symptoms such as fever and chills, indicative of the body’s robust inflammatory response. These symptoms often accompany the sudden onset of the condition and require prompt medical attention.
Etiology
Understanding the origins of prostatitis sheds light on its diverse forms and guides effective treatment strategies.
While acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis usually trace their roots to identifiable infectious causes, the etiology of chronic prostatitis, notably chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS), poses a more intricate puzzle. Despite extensive research, the precise origins of CP/CPPS remain elusive, prompting exploration into a spectrum of potential contributors.
-
Bacterial Infection
Although bacterial infection is a well-established cause of acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis, its role in CP/CPPS is more nuanced. Some theories suggest that low-grade or recurrent bacterial infections may contribute to the chronic inflammation seen in CP/CPPS cases.
-
Autoimmune Responses
The immune system’s response to the prostate itself is under scrutiny as a potential trigger for CP/CPPS. Autoimmune reactions, where the immune system mistakenly targets prostate tissues, could lead to the persistent inflammation and pain characteristic of this condition.
-
Neuromuscular Dysfunction
The intricate interplay between the nervous system and pelvic muscles introduces another layer of complexity. Neuromuscular dysfunction, which includes nerve signals that do not work right or muscle tension in the pelvic area, is thought to play a part in the cause of CP/CPPS. This dysfunction may amplify pain signals and contribute to people’s ongoing discomfort.
-
Psychosocial Factors
Emerging evidence highlights the role of psychosocial factors, including stress, anxiety, and past traumatic experiences, in influencing the onset and exacerbation of CP/CPPS. The intricate connection between the mind and the body underscores the need for a holistic approach to prostatitis management.
As research advances, a comprehensive understanding of these multifaceted contributors becomes pivotal for tailoring targeted interventions. Exploring the etiology of prostatitis not only enhances diagnostic precision but also informs a nuanced treatment approach, ranging from antibiotics and anti-inflammatories to stress management and neuromuscular therapies.
Diagnostic Challenges
Diagnosing prostatitis involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and often laboratory tests, including urine and prostate fluid analysis. Chronic prostatitis, with its ambiguous origins and varied presentations, poses diagnostic challenges, requiring a comprehensive evaluation.
Understanding prostatitis as a dynamic and diverse condition is pivotal for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment. The interplay between its various forms, coupled with the intricate relationship with conditions like Pudendal Neuralgia, emphasizes the need for a holistic approach to address the complexities of this prevalent male health concern.
Comprehensive Prostatitis Treatments
Effectively managing prostatitis demands a multifaceted approach, addressing underlying causes and alleviating diverse symptoms. Here’s an expert overview of key treatments:
-
Antibiotics for Bacterial Prostatitis
Antibiotics stand as the primary line of defense against bacterial prostatitis, tailored to the severity and type of infection. This targeted approach helps eradicate the underlying cause, promoting an efficient resolution.
-
Alpha Blockers, Especially Tamsulosin
Tamsulosin, an alpha blocker, plays a pivotal role in prostatitis management by relaxing muscles at the bladder-prostate junction. This action eases urinary symptoms, fostering enhanced comfort and functionality.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Primarily NSAIDs
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are instrumental in mitigating the pain and inflammation associated with prostatitis. This pharmacological intervention contributes to overall symptom relief.
-
Prostate Massage for Symptomatic Relief
Healthcare providers may recommend prostate massage, particularly in cases of chronic prostatitis. This hands-on approach aims to alleviate symptoms by promoting better fluid flow within the prostate, aiding in the reduction of discomfort.
-
Lifestyle Modifications for Holistic Well-being
Beyond pharmaceutical interventions, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in prostatitis management. Regular exercise not only contributes to overall health but also supports symptom alleviation. Stress management techniques and dietary adjustments, including the avoidance of irritants, further complement treatment efforts.
Incorporating these diverse prostatitis treatments into a comprehensive care plan ensures a holistic approach to symptom relief. Tailored interventions, ranging from antibiotics to lifestyle adjustments, empower individuals to navigate the complexities of prostatitis for optimal well-being. Explore these expert-recommended treatments to enhance your understanding and embrace a proactive approach to managing prostatitis.
Prostatitis-Pudendal Neuralgia Link
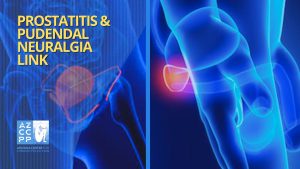
The connection between prostatitis and Pudendal Neuralgia reveals a complex relationship that significantly influences the experience of discomfort and pain in the pelvic region. Pudendal Neuralgia, a condition involving the pudendal nerve located in close proximity to the prostate, forms a crucial link in understanding the intricate landscape of male pelvic health.
Anatomically, the pudendal nerve’s proximity to the prostate allows for a direct impact on sensation and pain perception in this region, creating a dynamic interplay between these two conditions.
When prostatitis and Pudendal Neuralgia coexist, the symptoms may amplify, further complicating the clinical picture. Understanding this intricate connection is pivotal for devising holistic treatment strategies that address the multifaceted nature of pelvic discomfort.
By recognizing how the pudendal nerve influences sensation and pain in the prostate region, healthcare providers can tailor interventions that not only target the immediate symptoms but also address the underlying neural aspects contributing to the overall patient experience.
Incorporating this awareness into treatment plans enables a more comprehensive and effective approach to managing prostatitis and Pudendal Neuralgia concurrently. This holistic strategy acknowledges the anatomical nuances and interconnectedness of these conditions, fostering a more nuanced understanding of male pelvic health.
As we delve into the intricate realm of prostatitis and Pudendal Neuralgia, this knowledge empowers both healthcare providers and individuals to navigate the complexities of pelvic discomfort with a targeted and informed perspective.
Read More About Pudendal Neuralgia Here!
Comparing Prostatitis vs. BPH
Differentiating prostatitis from Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is essential for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment. Here’s a more detailed exploration of the key distinctions:
Etiology
- Prostatitis: Primarily stems from infection or inflammation within the prostate gland, with bacterial or non-bacterial origins.
- BPH: Results from age-related prostate enlargement, characterized by non-cancerous growth of prostate tissue.
Age of Onset
- Prostatitis: This can affect men of various age groups, including young and middle-aged individuals.
- BPH: More commonly observed in men over the age of 50, aligning with the natural aging process.
Treatment Focus
- Prostatitis: Targets infections and inflammation, involving antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and lifestyle modifications.
- BPH: Focuses on managing the enlargement of prostate tissue, with treatment options ranging from medications to surgical interventions.
Symptom Variation
- Prostatitis: May exhibit distinctive symptoms such as pelvic pain, discomfort, and systemic manifestations like fever, setting it apart from BPH.
- BPH: Typically characterized by urinary symptoms such as increased frequency, urgency, and difficulty in urination, without the pronounced pelvic pain associated with prostatitis.
Understanding these nuanced differences is crucial for healthcare professionals to formulate accurate diagnoses and tailor effective treatment plans. While both prostatitis and BPH share the stage in the realm of male reproductive health, recognizing their unique characteristics allows for a more precise approach to addressing the diverse needs of individuals experiencing these conditions.
Conclusion
Effective prostatitis treatment hinges on accurate diagnosis and comprehensive management strategies, including medication, lifestyle modifications, and, in some cases, procedural interventions. This is why distinguishing between prostatitis and BPH is crucial for appropriate management and treatment, given the overlapping symptoms but different underlying causes and treatment approaches. A thorough understanding of these conditions can empower individuals to seek timely and appropriate care, thereby improving their quality of life.

