S
Pelvic Floor Spasms are one of the most common conditions leading to both in women and in men.
This condition is one of the “evil quadruplets” since it tends to co-exist with endometriosis, / syndrome, and irritable syndrome. The condition is like having a charley horse in the muscles that surround the vagina, urethra, and . There are multiple reasons why this happens.

Most often, it is some other condition that, through complex neural mechanisms, is irritating the (s). Patients who have from endometriosis, , , or pelvic trauma may develop , which, unless treated, may last for many years. Some patients may also develop spasms after psychological trauma or even without any significant precipitating event.
Most commonly, patients with (s) will experience during intercourse, urination, and as well as any physical activity. Generally, this persists from hours to days after or . It may also persist after urination or . Patients with spasms may also have trouble starting the urine flow or difficulty in completely emptying the . Because of that incomplete emptying, they often get up at night multiple times to urinate.
(s) may be easily identified during a physical exam or exam by a trained physician or . Treatment consists of and relaxants.
The majority of patients are helped by those two modalities. In cases where is not relieved by and relaxants, botulinum toxin injections to the may be necessary. Treatment of the underlying is also very important.
In cases where developed because of other such as endometriosis, treatment of that underlying condition is very important. If someone has developed after placement of pelvic mesh, the mesh has to be addressed first before addressing .
At Arizona Center for , we work with physical therapists in the Phoenix area and throughout the United States. We strongly believe that is the most important part of relieving (s). In most cases, we will be able to recommend a in your area or provide you with resources to find one. Strengthening through is critical.
relaxants are usually used in the form of a vaginal or rectal suppository and seem to be more effective than oral medications. Different formulations of suppositories exist, and they will be discussed with you during the visit. Botulinum toxin A (BotoxÒ) injections are offered to patients when and suppositories fail. Those injections relieve spasms and in the great majority of patients, but they may need to be repeated every few months. Because those injections are painful, they should always be done under sedation.
If you have difficulty finding a in your area, please contact our office. We collaborate with therapists around the country, and we may be able to help you find one in your area. You can also visit the page of the International Society, the Women’s Section of the American Association, or Herman and Wallace Pelvic Rehabilitation Institute to find a provider in your area.
If you or someone you know is experiencing pain related to pelvic floor muscle spasms contact our office at 480 599-9682 or [email protected] to learn more about available treatments.
What to expect after BotoxÒ injection?
- BotoxÒ injections to pelvic floor muscles are almost always done in conjunction with pudendal nerve(s) block. The block is done to decrease pain after the procedure. When you wake up from the sedation after BotoxÒ injection, you will feel numbness in the pelvis, and you may have numbness in one or both of your legs. Numbness is completely normal and will disappear when the local anesthetic wears off.
- If you have numbness in your legs, you should avoid walking until the numbness goes away. You should have someone help you walk the first time you get up after the procedure.
- After the procedure, you may have difficulty emptying your bladder. Pelvic floor muscles are irritated immediately after the injection, and some patients may need a urinary catheter for a few days. Difficulty emptying the bladder goes away after BotoxÒ starts working and relaxes pelvic floor muscles.
- You may experience vaginal bleeding for 2-3 days after the procedure. It is completely normal, as long as the amount of bleeding is less than the menstrual period.
- After the local anesthetic wears off your pain may come back, and it may come back worse than it was before the procedure. This is because muscles are irritated from the injection. BotoxÒ starts working about one week after the procedure, but it may take 10-14 days to feel the relief of pain.
- It is very important to continue physical therapy after BotoxÒ Botulinum toxin by itself does not permanently cure muscle spasm, but it allows physical therapist to work more aggressively on your pelvic floor muscles.
- BotoxÒ wears off approximately 3-4 months after the injection. Some patients will not go back into spasm, but most will need a repeat injection. If you or your physical therapist feel your muscle spasm is returning, call our office to be scheduled for a repeat procedure.
Pelvic Floor Spasms
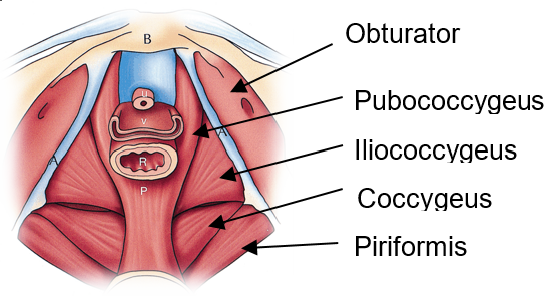
Pelvic floor dysfunction is a complex condition that encompasses a wide range of symptoms and abnormalities related to the pelvic floor. The pelvic floor, a supportive sling of muscles spanning the base of the pelvis, plays a pivotal role in the proper function of pelvic organs and the pelvic region. Dysfunction in this area can manifest in various ways, including hypertonic pelvic floor dysfunction, where the muscles of the pelvic floor remain persistently contracted, leading to pelvic muscle spasm or pelvic floor muscle spasm. This involuntary muscle tension can be distributed unevenly across the pelvic area, resulting in localized or generalized pelvic pain. Certain conditions like levator syndrome, caused by spasms in the levator ani muscle, and proctalgia fugax, an episodic, intense pain in the rectal area, are specific types of pelvic pain associated with pelvic floor muscle dysfunction. This hypertonicity can also negatively impact sexual function, with conditions like vaginismus, where the muscle spasm prevents or makes sexual intercourse painful. Moreover, disturbances in the pudendal nerve, which runs through the pelvic floor, can exacerbate or even initiate muscle spasms, thereby perpetuating chronic pain.
Many individuals suffering from pelvic floor disorders, including pelvic floor muscle spasms, experience challenges in their daily lives beyond pain. For instance, urinary incontinence and fecal incontinence, the involuntary loss of urine or stool, respectively, can result from abnormal muscle behavior or weakened connective tissue supporting the pelvic organs. Pelvic organ prolapse, where pelvic organs descend due to weakened support structures, is another consequence of pelvic floor disorder. Beyond these physical manifestations, the chronic pain and incontinence can significantly hinder one’s quality of life. Fortunately, therapeutic interventions such as pelvic floor physical therapy, overseen by a trained physical therapist, offer targeted exercises to strengthen, relax, and improve the coordination of the pelvic floor muscles. In more severe cases, muscle relaxants may be prescribed to alleviate persistent pelvic floor muscle spasms. Through a comprehensive approach addressing both the physical and emotional ramifications, individuals with pelvic floor dysfunction can find relief and reclaim control over their pelvic health.
Pelvic floor spasms, a subset of the broader condition known as pelvic floor dysfunction, refer to the involuntary and persistent contraction of the muscles located in the pelvic region. The pelvic floor musculature, comprising a complex web of muscles, ligaments, and connective tissue, plays a pivotal role in supporting the bladder, rectum, and other pelvic organs. When these muscles undergo undue tension or muscle spasms, it can lead to a variety of uncomfortable and sometimes painful symptoms. Patients might experience challenges during sexual intercourse due to muscle tension, leading to compromised sexual health and function. Additionally, an overactive bladder, urinary incontinence, and even symptoms similar to irritable bowel syndrome can manifest when the pelvic floor muscles are in persistent spasm. As these muscles are closely associated with the ani muscle, any dysfunction in this region can severely impact daily activities and overall well-being.
Addressing Pelvic Floor Spasms
To address pelvic floor spasms, it’s vital first to identify the root cause of the dysfunction. For some, the muscle tension might be a reaction to conditions like pelvic organ prolapse, where the pelvic organs descend due to weakened support structures. For others, it might be a standalone issue. Once identified, tailored interventions can be suggested. Pelvic floor exercises, often guided by trained physical therapists, aim at both strengthening and relaxing the pelvic floor muscles. This ensures that they function optimally, providing the necessary support without being perpetually tense. Manual therapy can also be a beneficial intervention, where therapists use hands-on techniques to release muscle tension and alleviate spasms. In more severe cases, muscle relaxants might be prescribed to combat persistent pelvic floor muscle dysfunction. An integrated approach, focusing on both symptomatic relief and addressing the underlying cause, ensures that individuals can regain control over their pelvic health, ensuring a balanced and functional pelvic area.
